We are changing our name from Blue Wolf to QIC Global
We are changing our name from Blue Wolf to QIC Global
Are your customers satisfied with the service you provide? Are you selling reliable medical devices? Enhance the quality of the devices with ISO 13485 certification. Get globally acknowledged by meeting the best industry practices!
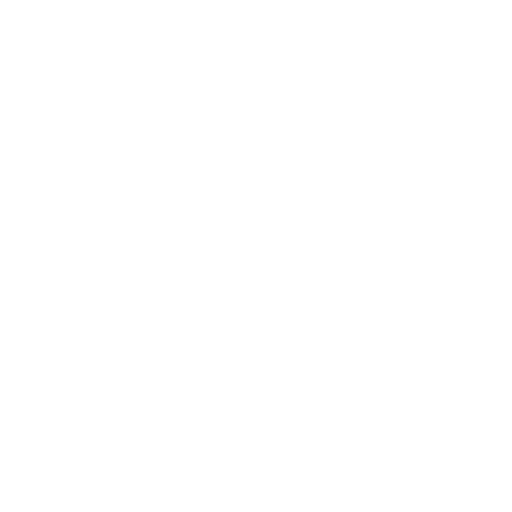




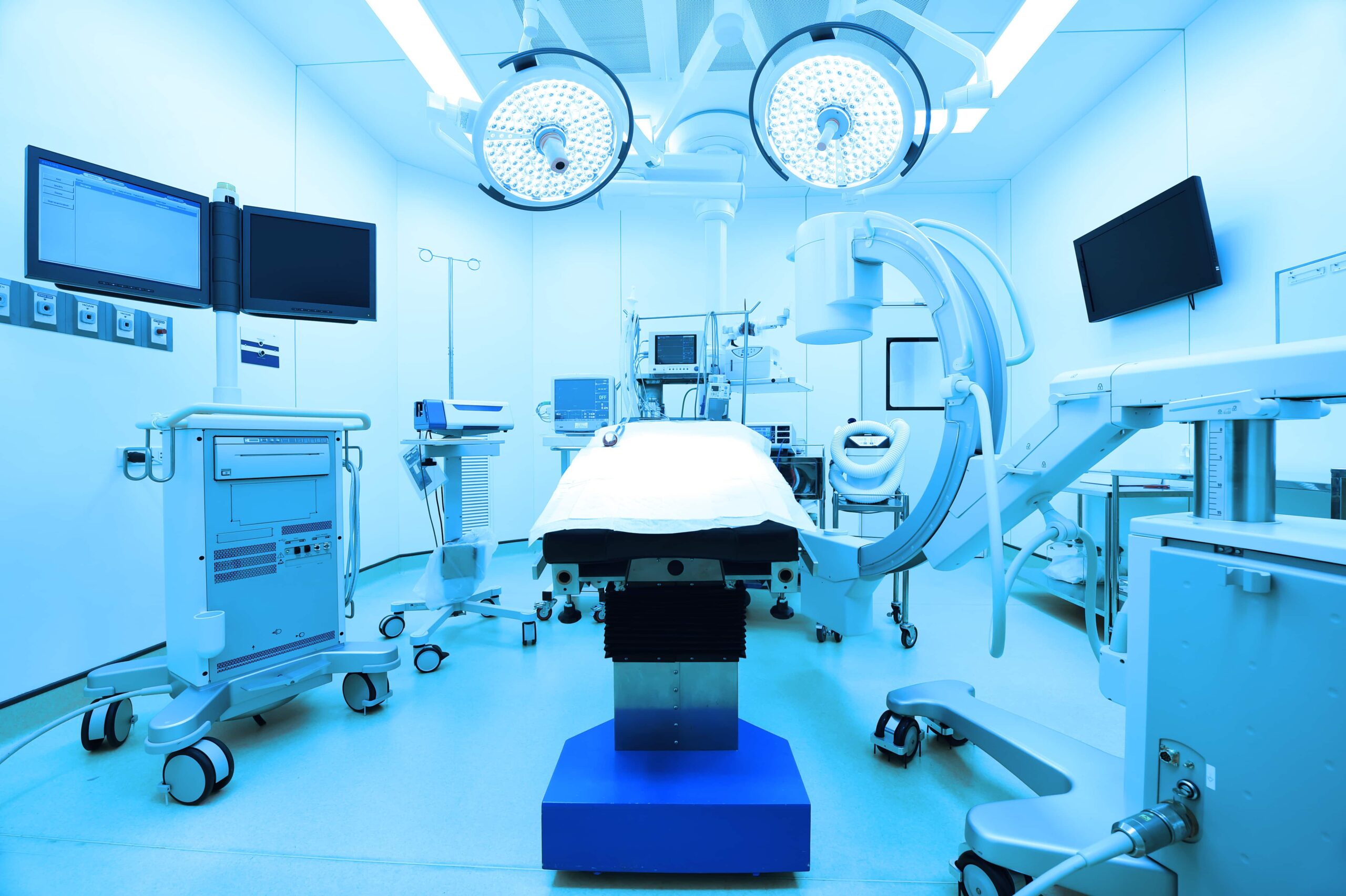
The ISO 13485 standard is widely known for offering a practical set of quality clauses to the medical device industry. Published in 1996 by the International Organization for Standardization, the standard went through several amendments until the latest version came in 2016. The standard aims to help companies in the medical device industry to effectively manufacture and supply premium-quality products. ISO 13485 sets guidelines, policies, and fundamental requirements to maintain an effective quality assurance program.
When it comes to quality management, the universally known and acknowledged benchmark is set by ISO 9001. ISO 13485 considers the predominant clauses designed by ISO 9001. The quality control standard for medical devices incorporates those clauses into its conditions. The adaptation of the original quality requirements gave a more descriptive shape to ISO 13485, which helps to maintain regulatory compliance as well.
The quality assurance/management business standards follow a “plan, do, check, act” protocol. It allows the companies to maintain a consistent process for designing, manufacturing, storing, supplying, installing, and disposing of medical devices. Companies eager to accomplish the certification must invest time in decoding the terms and definitions associated with the clauses. They must meet each clause to meet customer requirements and compliance.
The certification acts as a competitive shield for companies. It supports companies to acquire customer trust, which helps to strengthen the brand name and presence.
ISO 13485 certification helps to develop the best practices for manufacturing and supplying medical devices that augment medical recovery. Like any other quality management system, it provides the opportunity to detect internal system risks that can disrupt business operations. ISO 13485 is known for helping companies with the following aspects -

ISO 13485:2016 stipulates the requirements of a fully fledged Quality Management System (QMS) specific to the medical device design, development, production, installation, and servicing. To be compliant, organizations are required to:
Common audit deficiency findings are:
Such non-conformities may affect the safety of the products, their regulatory acceptance, and customer confidence.


“I want to express my sincere appreciation for your support during our recent ISO audit.”


“One of the best business decisions I think we've made in the entire time we've been here in the company.”


We make auditing your ISO Standards easy. We know audits can be stressful. We’ll take the stress out.


“What seemed like a very intimidating process … was made simple … and [has] elevated our quality and safety program to another level.”


“…our staff feel comfortable talking to [the auditor]… makes you feel like you are working together”


“…Relaxed, didn't feel pressured..."


“I would just say, if you want the best and you want to things done quickly and accurately that I’d go with Blue Wolf. The service was great. Again, just to the point, very speedy, not a lot of fluff around things. We just got to work and got it done and that was the objective.”


“Your approach [to the audit process] is by far superior than any other audit I’ve ever been through. The contrast was night and day”


“There was so much going on at the time of the audit that I just wanted to go back to the audit, it was more relaxing”


“I don’t ever want to experience an audit a different way”


“If everybody could have an audit experience like this, more and more people would actually consider an ISO certification”


“I learned a whole lot from what we just went through with [the auditor] that I didn’t even understand about the standard before”


“Our experience has been that this process in working with the auditors has shown us more ways to improve internally than what we expected”


“What seemed like a very intimidating process … was made simple … and [has] elevated our quality and safety program to another level.”


“…Relaxed, didn't feel pressured..."


“…our staff feel comfortable talking to [the auditor]… makes you feel like you are working together”


“It’s a very smooth and very clear process. Definitely recommended.”


"The auditor was very knowledgeable, very understanding, very helpful."


“Would give them a 10 out of 10 and would highly recommend them to anybody looking to get ISO certification in the future.”


“I found Blue Wolf to be the Cheapest and most experienced in my eyes ‘cause all of the price ranges were higher than Blue Wolf, so I stuck with Blue Wolf. Their quality was very high as well.”


“The service provided by Blue Wolf has been second to none.”


“Blue Wolf streamlined the entire process. They were very easy to communicate with and work with, very cordial, and just an all-around good experience.”


“Blue Wolf makes a great partner for not only getting but maintaining your ISO certifications.”
Quality Management Systems
Environmental Management Systems
Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems
Information Security Management Systems
The Information Technology (IT) Service Management System Standard for earning global recognition!
Global Quality Management Standard for Medical Devices
Energy Management System efficiency
Food Safety Management Systems
Anti-Bribery Management System
Business continuity management system
The Privacy Management Standard for corporate documents
The education management standard for a better learning experience!